TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
Deletion in Circular Doubly Linked List at End
Deletion in Circular Doubly Linked List at End with Introduction, Asymptotic Analysis, Array, Pointer, Structure, Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List, Binary Search, Linear Search, Sorting, Bucket Sort, Comb Sort, Shell Sort, Heap Sort, Merge Sort, Selection Sort, Counting Sort, Stack, Qene, Circular Quene, Graph, Tree, B Tree, B+ Tree, Avl Tree etc.
Deletion in circular doubly linked list at endThere can be two scenario of deleting the first node in a circular doubly linked list. The node which is to be deleted can be the only node present in the linked list. In this case, the condition head → next == head will become true, therefore the list needs to be completely deleted. It can be simply done by assigning head pointer of the list to null and free the head pointer. head = NULL; free(head); in the second scenario, the list contains more than one element in the list, therefore the condition head → next == head will become false. Now, reach the last node of the list and make a few pointer adjustments there. Run a while loop for this purpose
temp = head;
while(temp -> next != head)
{
temp = temp -> next;
}
Now, temp will point to the node which is to be deleted from the list. Make the next pointer of previous node of temp, point to the head node of the list. temp -> prev -> next = head; make the previous pointer of the head node, point to the previous node of temp. head -> prev = ptr -> prev; Now, free the temp pointer to free the memory taken by the node. free(head) in this way, the last node of the list is deleted. Algorithm
Write UNDERFLOW [END OF LOOP] 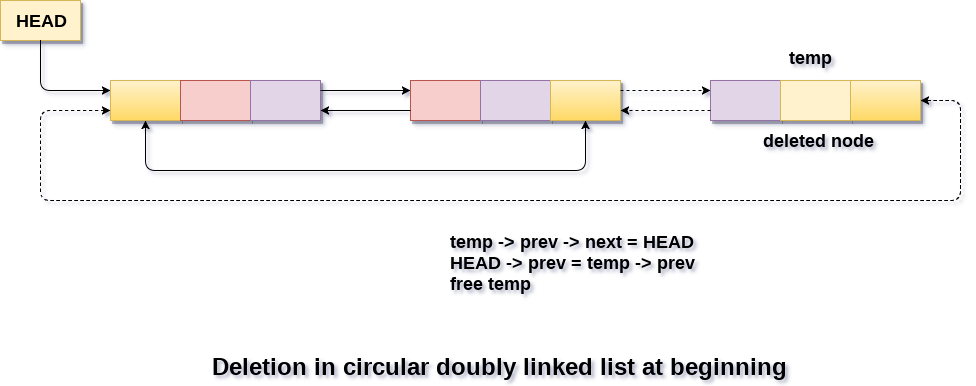
C Function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void create(int);
void deletion_last();
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
struct node *head;
void main ()
{
int choice,item;
do
{
printf("1.Append List\n2.Delete Node from last\n3.Exit\n4.Enter your choice?");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the item\n");
scanf("%d",&item);
create(item);
break;
case 2:
deletion_last();
break;
case 3:
exit(0);
break;
default:
printf("\nPlease Enter valid choice\n");
}
}while(choice != 3);
}
void create(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *temp;
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("\nOVERFLOW\n");
}
else
{
ptr->data=item;
if(head == NULL)
{
head = ptr;
ptr -> next = head;
ptr -> prev = head;
}
else
{
temp = head;
while(temp->next !=head)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = ptr;
ptr ->prev=temp;
head -> prev = ptr;
ptr -> next = head;
}
}
printf("\nNode Inserted\n");
}
void deletion_last()
{
struct node *ptr;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("\n UNDERFLOW\n");
}
else if(head->next == head)
{
head = NULL;
free(head);
printf("\nNode Deleted\n");
}
else
{
ptr = head;
if(ptr->next != head)
{
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
ptr -> prev -> next = head;
head -> prev = ptr -> prev;
free(ptr);
printf("\nNode Deleted\n");
}
}
Output 1.Append List 2.Delete Node from last 3.Exit 4.Enter your choice?1 Enter the item 12 Node Inserted 1.Append List 2.Delete Node from last 3.Exit 4.Enter your choice?2 Node Deleted
Next TopicDoubly Linked List
|
Related Links:
- Deletion in Doubly Linked List at The End
- Deletion in Doubly Linked List After The Specified Node
- Deletion in Circular Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Deletion in Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Deletion in Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Deletion in Binary Search Tree
- Deletion in AVL Tree
- Deletion in Circular Singly Linked List at End
- Deletion in Singly Linked List at End
- Deletion in Singly Linked List After Specified Node
- Deletion in Circular Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Deletion in Circular Doubly Linked List at End

