TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at End
Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at End with Introduction, Asymptotic Analysis, Array, Pointer, Structure, Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List, Binary Search, Linear Search, Sorting, Bucket Sort, Comb Sort, Shell Sort, Heap Sort, Merge Sort, Selection Sort, Counting Sort, Stack, Qene, Circular Quene, Graph, Tree, B Tree, B+ Tree, Avl Tree etc.
Insertion into circular singly linked list at the endThere are two scenario in which a node can be inserted in circular singly linked list at beginning. Either the node will be inserted in an empty list or the node is to be inserted in an already filled list. struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); In the first scenario, the condition head == NULL will be true. Since, the list in which, we are inserting the node is a circular singly linked list, therefore the only node of the list (which is just inserted into the list) will point to itself only. We also need to make the head pointer point to this node. This will be done by using the following statements.
if(head == NULL)
{
head = ptr;
ptr -> next = head;
}
In the second scenario, the condition head == NULL will become false which means that the list contains at least one node. In this case, we need to traverse the list in order to reach the last node of the list. This will be done by using the following statement. temp = head; while(temp->next != head) temp = temp->next; At the end of the loop, the pointer temp would point to the last node of the list. Since, the new node which is being inserted into the list will be the new last node of the list. Therefore the existing last node i.e. temp must point to the new node ptr. This is done by using the following statement. temp -> next = ptr; The new last node of the list i.e. ptr will point to the head node of the list. ptr -> next = head; In this way, a new node will be inserted in a circular singly linked list at the beginning. Algorithm
Write OVERFLOW [END OF LOOP] 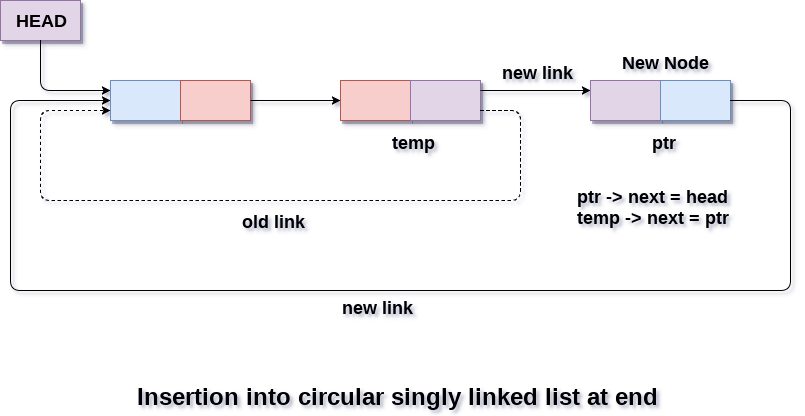
C Function
void lastinsert(struct node*ptr, struct node *temp, int item)
{
ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("\nOVERFLOW\n");
}
else
{
ptr->data = item;
if(head == NULL)
{
head = ptr;
ptr -> next = head;
}
else
{
temp = head;
while(temp -> next != head)
{
temp = temp -> next;
}
temp -> next = ptr;
ptr -> next = head;
}
}
}
Next TopicDoubly Linked List
|
Related Links:
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List at The End
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List After Specified Node
- Insertion in Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Binary Search Tree
- Insertion in AVL Tree
- Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List at End
- Insertion in Singly Linked List at End
- Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at End
- Insertion Sort
- Insertion in Singly Linked List After Specified Node

