TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
Insertion in Doubly Linked List After Specified Node
Insertion in Doubly Linked List After Specified Node with Introduction, Asymptotic Analysis, Array, Pointer, Structure, Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List, Binary Search, Linear Search, Sorting, Bucket Sort, Comb Sort, Shell Sort, Heap Sort, Merge Sort, Selection Sort, Counting Sort, Stack, Qene, Circular Quene, Graph, Tree, B Tree, B+ Tree, Avl Tree etc.
Insertion in doubly linked list after Specified nodeIn order to insert a node after the specified node in the list, we need to skip the required number of nodes in order to reach the mentioned node and then make the pointer adjustments as required. Use the following steps for this purpose.
ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp=head;
for(i=0;i<loc;i++)
{
temp = temp->next;
if(temp == NULL) // the temp will be //null if the list doesn't last long //up to mentioned location
{
return;
}
}
ptr → next = temp → next; make the prev of the new node ptr point to temp. ptr → prev = temp; make the next pointer of temp point to the new node ptr. temp → next = ptr; make the previous pointer of the next node of temp point to the new node. temp → next → prev = ptr; Algorithm
Write OVERFLOW 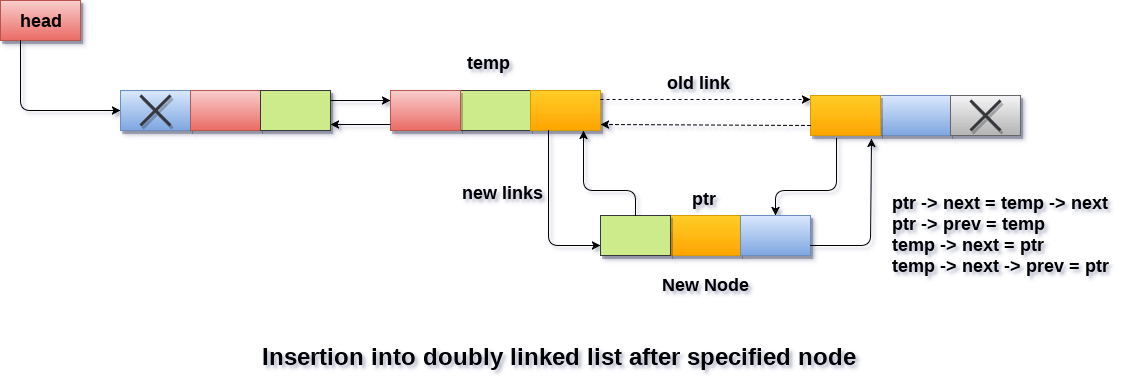
C Function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void insert_specified(int);
void create(int);
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
struct node *head;
void main ()
{
int choice,item,loc;
do
{
printf("\nEnter the item which you want to insert?\n");
scanf("%d",&item);
if(head == NULL)
{
create(item);
}
else
{
insert_specified(item);
}
printf("\nPress 0 to insert more ?\n");
scanf("%d",&choice);
}while(choice == 0);
}
void create(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("\nOVERFLOW");
}
else
{
if(head==NULL)
{
ptr->next = NULL;
ptr->prev=NULL;
ptr->data=item;
head=ptr;
}
else
{
ptr->data=item;printf("\nPress 0 to insert more ?\n");
ptr->prev=NULL;
ptr->next = head;
head->prev=ptr;
head=ptr;
}
printf("\nNode Inserted\n");
}
}
void insert_specified(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *temp;
int i, loc;
if(ptr == NULL)
{
printf("\n OVERFLOW");
}
else
{
printf("\nEnter the location\n");
scanf("%d",&loc);
temp=head;
for(i=0;i<loc;i++)
{
temp = temp->next;
if(temp == NULL)
{
printf("\ncan't insert\n");
return;
}
}
ptr->data = item;
ptr->next = temp->next;
ptr -> prev = temp;
temp->next = ptr;
temp->next->prev=ptr;
printf("Node Inserted\n");
}
}
Output Enter the item which you want to insert? 12 Node Inserted Press 0 to insert more ? 0 Enter the item which you want to insert? 90 Node Inserted Press 0 to insert more ? 2
Next TopicDoubly Linked List
|
Related Links:
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List at The End
- Insertion in Doubly Linked List After Specified Node
- Insertion in Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Binary Search Tree
- Insertion in AVL Tree
- Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Circular Doubly Linked List at End
- Insertion in Singly Linked List at End
- Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at Beginning
- Insertion in Circular Singly Linked List at End
- Insertion Sort
- Insertion in Singly Linked List After Specified Node