TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
DS Array
DS Array with Introduction, Asymptotic Analysis, Array, Pointer, Structure, Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List, Binary Search, Linear Search, Sorting, Bucket Sort, Comb Sort, Shell Sort, Heap Sort, Merge Sort, Selection Sort, Counting Sort, Stack, Qene, Circular Quene, Graph, Tree, B Tree, B+ Tree, Avl Tree etc.
ArrayDefinition
The array marks[10] defines the marks of the student in 10 different subjects where each subject marks are located at a particular subscript in the array i.e. marks[0] denotes the marks in first subject, marks[1] denotes the marks in 2nd subject and so on. Properties of the Array
for example, in C language, the syntax of declaring an array is like following: int arr[10]; char arr[10]; float arr[5] Need of using Array
In computer programming, the most of the cases requires to store the large number of data of similar type. To store such amount of data, we need to define a large number of variables. It would be very difficult to remember names of all the variables while writing the programs. Instead of naming all the variables with a different name, it is better to define an array and store all the elements into it. Following example illustrates, how array can be useful in writing code for a particular problem. In the following example, we have marks of a student in six different subjects. The problem intends to calculate the average of all the marks of the student. In order to illustrate the importance of array, we have created two programs, one is without using array and other involves the use of array to store marks. Program without array:
#include <stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int marks_1 = 56, marks_2 = 78, marks_3 = 88, marks_4 = 76, marks_5 = 56, marks_6 = 89;
float avg = (marks_1 + marks_2 + marks_3 + marks_4 + marks_5 +marks_6) / 6 ;
printf(avg);
}
Program by using array:
#include <stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int marks[6] = {56,78,88,76,56,89);
int i;
float avg;
for (i=0; i<6; i++ )
{
avg = avg + marks[i];
}
printf(avg);
}
Complexity of Array operationsTime and space complexity of various array operations are described in the following table. Time Complexity
Space ComplexityIn array, space complexity for worst case is O(n). Advantages of Array
Memory Allocation of the arrayAs we have mentioned, all the data elements of an array are stored at contiguous locations in the main memory. The name of the array represents the base address or the address of first element in the main memory. Each element of the array is represented by a proper indexing. The indexing of the array can be defined in three ways.
In the following image, we have shown the memory allocation of an array arr of size 5. The array follows 0-based indexing approach. The base address of the array is 100th byte. This will be the address of arr[0]. Here, the size of int is 4 bytes therefore each element will take 4 bytes in the memory. 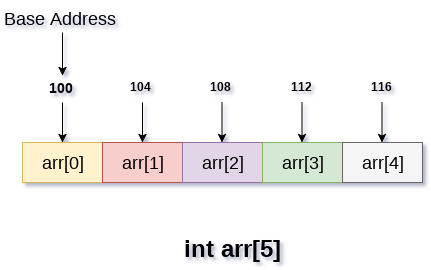
In 0 based indexing, If the size of an array is n then the maximum index number, an element can have is n-1. However, it will be n if we use 1 based indexing. Accessing Elements of an arrayTo access any random element of an array we need the following information:
Address of any element of a 1D array can be calculated by using the following formula: Byte address of element A[i] = base address + size * ( i - first index) Example : In an array, A[-10 ..... +2 ], Base address (BA) = 999, size of an element = 2 bytes, find the location of A[-1]. L(A[-1]) = 999 + [(-1) - (-10)] x 2 = 999 + 18 = 1017 Passing array to the function :As we have mentioned earlier that, the name of the array represents the starting address or the address of the first element of the array. All the elements of the array can be traversed by using the base address. The following example illustrate, how the array can be passed to a function. Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int summation(int[]);
void main ()
{
int arr[5] = {0,1,2,3,4};
int sum = summation(arr);
printf("%d",sum);
}
int summation (int arr[])
{
int sum=0,i;
for (i = 0; i<5; i++)
{
sum = sum + arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
The above program defines a function named as summation which accepts an array as an argument. The function calculates the sum of all the elements of the array and returns it.
Next Topic2D Array
|
Related Links:
- Data Mining Architecture
- Data Structures | DS Tutorial
- Computer Network | Data Link Controls
- DS for symbols tables
- Data Preprocessing in Machine learning
- Data Mining Tools
- Data Mining vs Machine Learning
- What is Data Science: Tutorial, Components, Tools, Life Cycle, Applications
- DS Algorithm
- DS Asymptotic Analysis
- Data Flow in Angular 7 Forms
- Data Mining Tutorial
- Data Mining Cluster Analysis
- Data Mining vs Data Warehousing
- DS Structure
- DS Array
- DS 2D Array
- DS Quene
- Different types of Clustering Algorithm
- Data Mining vs Big Data
- Data Mining Bayesian Classification
- Data Mining World Wide Web
- Data Types in C
- Verbal Reasoning | Data Sufficiency 2
- Data Mining Techniques
- DS Introduction
- Data Structure Interview Questions (2021)
- Verbal Reasoning | Data Sufficiency 1
- Top 25 Data Science Interview Questions (2021)
- Data Warehouse Tutorial
- Data Flow in MapReduce
- DS Stack
- Data Abstraction in C++
- Top 25 Data Warehouse Interview Questions (2021)
- Data Link layer
- Data Security Considerations
- DS Pointer


