TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
PHP MVC Architecture
PHP MVC Architecture for beginners and professionals with examples, php file, php session, php date, php array, php form, functions, time, xml, ajax, php mysql, regex, string, oop, chop(), bin2hex(), addslashes(), addcslashes() etc.
MVC ArchitectureMVC is a software architectural pattern for implementing user interfaces on computers. It divides a given application into three interconnected parts. This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to, and accepted from the user.
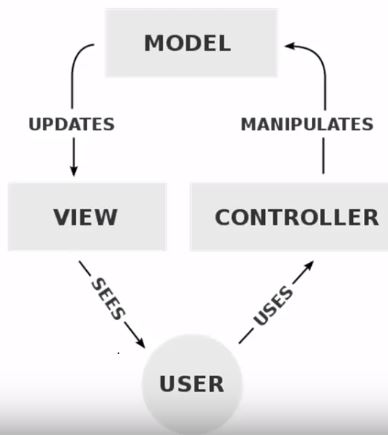
Model: Database operation such as fetch data or update data etc. View: End-user GUI through which user can interact with system, i.e., HTML, CSS. Controller: Contain Business logic and provide a link between model and view. Let's understand this MVC concept in detail: Model:
View:
Controller:
Next TopicPHP v/s JavaScript
|
Related Links:
- PHP Data Types
- PHP operators
- PHP Programs
- PHP Functions
- PHP Parameterized Function
- PHP Variable Length Argument Function
- What is PHP PDO: Tutorial, Advantages, Installation, Database Connection
- PHP Echo
- PHP Include File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Print
- PHP Variables
- PHP $ and $$
- PHP Constants
- PHP comments
- PHP If Else
- PHP Switch
- PHP For Loop
- PHP while loop
- PHP do while loop
- PHP Call By Value
- PHP File
- PHP Call By Reference
- PHP Default Argument Values Function
- PHP MySQL Login System
- PHP Recursive Function
- PHP Array
- PHP Indexed Array
- PHP Associative Array
- PHP MongoDB Example
- PHP Multidimensional Array
- PHP Array Functions
- PHP Strings
- PHP String Functions
- PHP Form
- PHP Cookie
- PHP Session
- PHP Open File
- PHP Read File
- PHP Write File
- PHP vs. HTML
- PHP vs Node.js
- PHP vs. Python
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Download File
- PHP MVC Architecture
- PHP vs. JavaScript
- PHP Append to File
- Learn PHP Tutorial
- PHP require_once
- PHP include_once
- PHP MySQL Connect
- PHP MySQL Create Database
- PHP MySQL Create Table
- PHP Math
- PHP MySQL Insert
- PHP MySQL Update
- PHP MySQL Delete
- PHP Example
- PHP Magic Constants
- PHP break
- PHP Mail
- PHP MySQL Select
- PHP MySQL Order By
- PHP JSON
- Top 69 PHP Interview Questions (2021)


