TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
C Expressions
C Expressions with Tutorial or what is c programming, C language with programming examples for beginners and professionals covering concepts, control statements, c array, c pointers, c structures, c union, c strings and more.
C ExpressionsAn expression is a formula in which operands are linked to each other by the use of operators to compute a value. An operand can be a function reference, a variable, an array element or a constant. Let's see an example: a-b; In the above expression, minus character (-) is an operator, and a, and b are the two operands. There are four types of expressions exist in C:
Each type of expression takes certain types of operands and uses a specific set of operators. Evaluation of a particular expression produces a specific value. For example: x = 9/2 + a-b; The entire above line is a statement, not an expression. The portion after the equal is an expression. 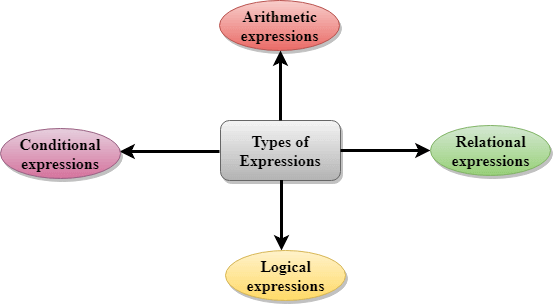
Arithmetic Expressions
An arithmetic expression is an expression that consists of operands and arithmetic operators. An arithmetic expression computes a value of type int, float or double. When an expression contains only integral operands, then it is known as pure integer expression when it contains only real operands, it is known as pure real expression, and when it contains both integral and real operands, it is known as mixed mode expression. Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions The expressions are evaluated by performing one operation at a time. The precedence and associativity of operators decide the order of the evaluation of individual operations. When individual operations are performed, the following cases can be happened:
Let's understand through an example. 6*2/ (2+1 * 2/3 + 6) + 8 * (8/4)
Relational Expressions
Let's see a simple example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x=4;
if(x%2==0)
{
printf("The number x is even");
}
else
printf("The number x is not even");
return 0;
}
Output 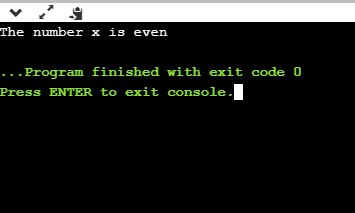
Logical Expressions
Let's see some example of the logical expressions.
Let's see a simple program of "&&" operator.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int y = 10;
if ( (x <10) && (y>5))
{
printf("Condition is true");
}
else
printf("Condition is false");
return 0;
}
Output 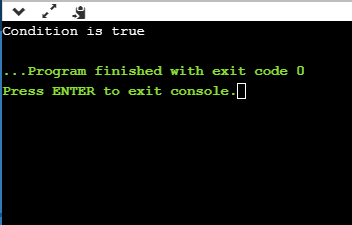
Let's see a simple example of "| |" operator
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int y = 9;
if ( (x <6) || (y>10))
{
printf("Condition is true");
}
else
printf("Condition is false");
return 0;
}
Output 
Conditional Expressions
The Syntax of Conditional operator Suppose exp1, exp2 and exp3 are three expressions. exp1 ? exp2 : exp3 The above expression is a conditional expression which is evaluated on the basis of the value of the exp1 expression. If the condition of the expression exp1 holds true, then the final conditional expression is represented by exp2 otherwise represented by exp3. Let's understand through a simple example.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
int age = 25;
char status;
status = (age>22) ? 'M': 'U';
if(status == 'M')
printf("Married");
else
printf("Unmarried");
return 0;
}
Output 
Next TopicData Segments
|
Related Links:
- C# this
- C# static
- C# static class
- C# static constructor
- C# Main Thread
- C# Thread Sleep
- C# Structs
- C# Enum
- C# Properties
- C# Aggregation
- C# Member Overloading
- C# Method Overriding
- C# Base
- Learn C Programming Language Tutorial
- C# Polymorphism
- C# Sealed
- C# Abstract
- C# Interface
- C# Access Modifiers
- C# Namespaces
- C# Encapsulation
- C# Strings
- C# Exception Handling
- C# try-catch
- C# finally
- C# User Defined Exceptions
- C# Checked and Unchecked
- C# SystemException
- C# FileStream
- C# StreamWriter
- C# StreamReader
- C# TextWriter
- C# TextReader
- C# BinaryWriter
- C# FileInfo
- C# DirectoryInfo
- C# BinaryReader
- C# StringWriter
- C# StringReader
- C# Serialization
- C# Deserialization
- C# System.IO Namespace
- C# Collections
- C# List
- C# HashSet
- C# SortedSet
- C# Stack
- C# Queue
- C# LinkedList
- C# Dictionary
- C# Inheritance
- C# SortedDictionary
- C# SortedList
- C# Generics
- C# Delegates
- C# Reflection
- C# Anonymous Function
- C# Multithreading
- C# Thread Life Cycle
- C# Thread Class
- C# Threading Example
- C# Thread Abort
- C# ThreadPriority
- C# Thread Synchronization | C# Lock
- C Identifiers
- C Switch Statement
- C break statement
- C Array
- C Operators
- C Format Specifier
- C Pointers
- C Pointer to Pointer
- C if else statement
- C Programming Interview Questions (2021)
- C Loop
- C# Jagged Arrays
- C continue statement
- C goto statement
- C String Functions
- C strlen() function
- C strcpy() function
- C strcat() function
- C Union
- C vs C++
- Top 26 C# Interview Questions (2021)
- C strcmp() function
- C strrev() function
- C strlwr() function
- C strupr() function
- C strstr() function
- C Math Functions
- C# Thread Join
- C# Thread Name
- C Preprocessor
- C Macros
- C #include
- C #define
- C #undef
- C #ifdef
- C #ifndef
- C #if
- C #else
- C #error
- Learn C# Tutorial
- C #pragma
- C Expressions
- C Data Segments
- C Programs
- C# if else
- C# Do While Loop
- C Program to reverse number
- C Program to swap two numbers without using third variable
- C Program to print hello without semicolon
- C Program without main()
- C Program to print Alphabet Triangle
- C# Example
- C Program to convert Decimal to Binary
- C Program to convert Number in Characters
- C Strings
- C gets() and puts()
- C Program to print Number Triangle
- C Program to generate Fibonacci Triangle
- C# switch
- C# For Loop
- C# While Loop
- C# Break Statement
- C# Continue Statement
- C# Array to Function
- C# Multidimensional Array
- C# Goto Statement
- C# Comments
- C# Function
- C# Call By Value
- C# Call By Reference
- C# Out Parameter
- C# Arrays
- C# Params
- C# Array Class
- C# Command Line Arguments
- C# Object and Class
- C# Constructor
- C# Destructor