TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
DBMS Schedule
DBMS Schedule with DBMS Overview, DBMS vs Files System, DBMS Architecture, Three schema Architecture, DBMS Language, DBMS Keys, DBMS Generalization, DBMS Specialization, Relational Model concept, SQL Introduction, Advantage of SQL, DBMS Normalization, Functional Dependency, DBMS Schedule, Concurrency Control etc.
ScheduleA series of operation from one transaction to another transaction is known as schedule. It is used to preserve the order of the operation in each of the individual transaction. 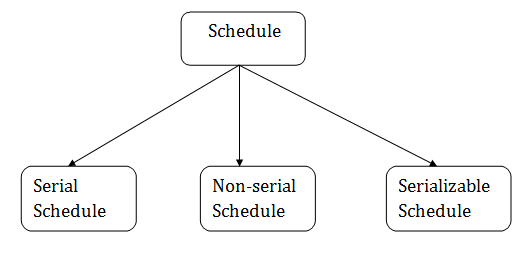
1. Serial Schedule
The serial schedule is a type of schedule where one transaction is executed completely before starting another transaction. In the serial schedule, when the first transaction completes its cycle, then the next transaction is executed. For example: Suppose there are two transactions T1 and T2 which have some operations. If it has no interleaving of operations, then there are the following two possible outcomes:
2. Non-serial Schedule
3. Serializable schedule
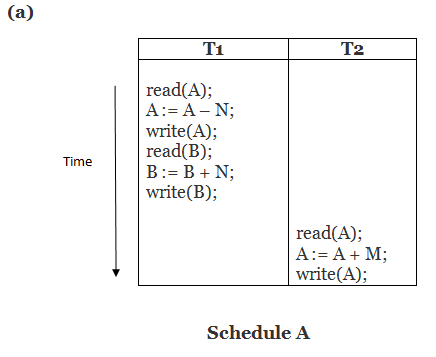
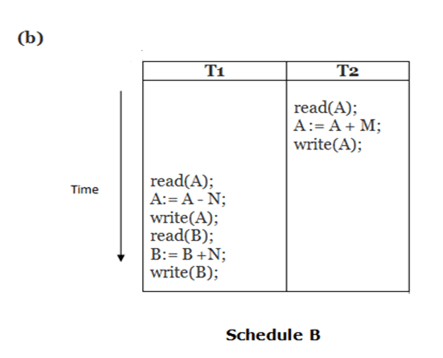
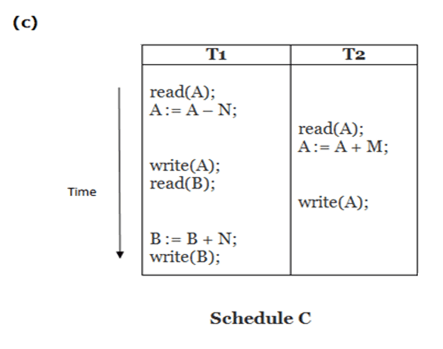
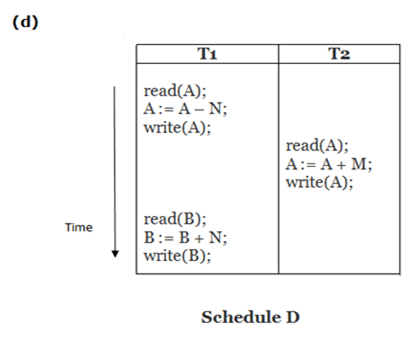
Here, Schedule A and Schedule B are serial schedule. Schedule C and Schedule D are Non-serial schedule.
Next TopicDBMS Testing of Serializability
|
Related Links:
- DBMS Multivalued Dependency
- DBMS Inclusion Dependence
- DBMS SQL Set Operation
- Top 52 DBMS Interview Questions (2021)
- DBMS Transaction Processing Concept
- DBMS States of Transaction
- DBMS Schedule
- DBMS Conflict Serializable Schedule
- DBMS View Serializability
- DBMS Recoverability of Schedule
- DBMS Tutorial | Database Management System
- DBMS Failure Classification
- DBMS Concurrency Control
- DBMS Lock based Protocol
- DBMS Log-Based Recovery
- DBMS Checkpoint
- DBMS Timestamp Ordering Protocol
- DBMS Validation based Protocol
- DBMS Thomas Write Rule
- DBMS Multiple Granularity
- DBMS Sequential File Organization
- DBMS Recovery Concurrent Transaction
- DBMS Characteristics of SQL
- DBMS File organization
- DBMS Heap File Organization
- DBMS Hash File Organization
- DBMS B+ Tree
- DBMS RAID
- DBMS B+ File Organization
- DBMS Indexed Sequential Access Method
- DBMS Cluster File Organization
- DBMS Hashing
- DBMS Static Hashing
- DBMS Dynamic Hashing
- DBMS SQL Introduction
- DBMS Advantage of SQL
- SQL Commands: DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, DQL
- DBMS SQL Operator
- DBMS SQL Insert
- DBMS SQL Update
- DBMS SQl Datatype
- DBMS SQL Table
- DBMS SQL Select
- DBMS SQL Index
- DBMS SQL Sub Queries
- DBMS SQL Clauses
- DBMS Generalization
- DBMS Specialization
- DBMS vs Files System
- DBMS Architecture
- DBMS SQL Delete
- DBMS SQL View
- DBMS Three schema Architecture
- DBMS Data model schema and Instance
- DBMS Join Operation
- DBMS Notation for ER diagram
- DBMS Relational Calculus
- DBMS Data Independence
- DBMS Language
- DBMS ER model concept
- DBMS Mapping constraints
- DBMS Keys: Primary, Foreign, Candidate and Super Key
- DBMS Aggregation
- DBMS Join Dependency
- DBMS Convert ER into table
- DBMS Relationship of Higher Degree
- DBMS Relational Model concept
- DBMS Relational Algebra
- DBMS Integrity Constraints
- DBMS Functional Dependency
- DBMS Inference Rule
- DBMS Normalization: 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF with Examples
- DBMS Transaction Property
- DBMS Testing of Serializability
- DBMS 1NF
- DBMS 2NF
- DBMS SQL Aggregate function
- DBMS SQL Joins
- DBMS 3NF
- DBMS BCNF
- DBMS 4NF
- DBMS 5NF
- DBMS Relational Decomposition


