TheDeveloperBlog.com
C-Sharp | Java | Python | Swift | GO | WPF | Ruby | Scala | F# | JavaScript | SQL | PHP | Angular | HTML
JavaScript Cookie Attributes
JavaScript Cookie Attributes with javascript tutorial, introduction, javascript oops, application of javascript, loop, variable, data types, operators, javascript if, switch, operators, objects, form validation, map, typedarray etc.
Cookie AttributesJavaScript provides some optional attributes that enhance the functionality of cookies. Here, is the list of some attributes with their description.
Cookie expires attribute
The cookie expires attribute provides one of the ways to create a persistent cookie. Here, a date and time are declared that represents the active period of a cookie. Once the declared time is passed, a cookie is deleted automatically. Let's see an example of cookie expires attribute.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="setCookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="getCookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="username=Duke Martin;expires=Sun, 20 Aug 2030 12:00:00 UTC";
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
var array=document.cookie.split("=");
alert("Name="+array[0]+" "+"Value="+array[1]);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Cookie max-age attribute
The cookie max-age attribute provides another way to create a persistent cookie. Here, time is declared in seconds. A cookie is valid up to the declared time only. Let's see an example of cookie max-age attribute.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="setCookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="getCookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="username=Duke Martin;max-age=" + (60 * 60 * 24 * 365) + ";"
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
var array=document.cookie.split("=");
alert("Name="+array[0]+" "+"Value="+array[1]);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Cookie path attribute
If a cookie is created for a webpage, by default, it is valid only for the current directory and sub-directory. JavaScript provides a path attribute to expand the scope of cookie up to all the pages of a website. Cookie path attribute ExampleLet's understand the path attribute with the help of an example. 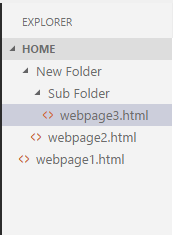
Here, if we create a cookie for webpage2.html, it is valid only for itself and its sub-directory (i.e., webpage3.html). It is not valid for webpage1.html file. In this example, we use path attribute to enhance the visibility of cookies up to all the pages. Here, you all just need to do is to maintain the above directory structure and put the below program in all three web pages. Now, the cookie is valid for each web page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" value="setCookie" onclick="setCookie()">
<input type="button" value="getCookie" onclick="getCookie()">
<script>
function setCookie()
{
document.cookie="username=Duke Martin;max-age=" + (60 * 60 * 24 * 365) + ";path=/;"
}
function getCookie()
{
if(document.cookie.length!=0)
{
var array=document.cookie.split("=");
alert("Name="+array[0]+" "+"Value="+array[1]);
}
else
{
alert("Cookie not available");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Cookie domain attributeA JavaScript domain attribute specifies the domain for which the cookie is valid. Let's suppose if we provide any domain name to the attribute such like: domain=TheDeveloperBlog.com Here, the cookie is valid for the given domain and all its sub-domains. However, if we provide any sub-domain to the attribute such like: omain=training.TheDeveloperBlog.com Here, the cookie is valid only for the given sub-domain. So, it's a better approach to provide domain name instead of sub-domain.
Next TopicCookie with multiple Name
|
Related Links:
- JavaScript Hoisting
- JavaScript Object, Dictionary Examples
- JavaScript String concat Example
- JavaScript number
- JavaScript Math round() Method
- JavaScript Boolean
- JavaScript Math sign() Method
- JavaScript OOPs Prototype Object
- JavaScript OOPs Inheritance
- JavaScript Math sin() Method
- JavaScript history object
- JavaScript navigator object
- JavaScript Math sinh() Method
- JavaScript screen
- JavaScript Math sqrt() Method
- JavaScript Math tan() Method
- JavaScript - innerHTML property
- JavaScript Math tanh() Method
- JavaScript - innerText property
- JavaScript form validation
- JavaScript OOPs Classes
- JavaScript Math trunc() Method
- JavaScript Number isFinite() Method
- JavaScript Number isInteger() Method
- JavaScript Number parseFloat() Method
- JavaScript Number parseInt() Method
- JavaScript Number toExponential() Method
- JavaScript Number toFixed() Method
- JavaScript Number toPrecision() Method
- JavaScript Number toString() Method
- JavaScript RegExp exec() Method
- JavaScript OOPs Constructor Method
- JavaScript OOPs Static Method
- JavaScript OOPs Encapsulation
- JavaScript OOPs Polymorphism
- JavaScript OOPs Abstraction
- JavaScript Cookies
- JavaScript Cookie Attributes
- JavaScript Cookie with multiple Name
- JavaScript Deleting a Cookie
- Not Found: javascript-date-setmonth-method
- JavaScript String lastIndexOf() Method
- JavaScript This Keyword
- JavaScript function Examples
- JavaScript Debugging
- JavaScript Strict Mode
- JavaScript TypedArray
- JavaScript Set
- JavaScript RegExp test() Method
- JavaScript Object assign() Method
- JavaScript RegExp toString() Method
- JavaScript Object create() Method
- JavaScript Object defineProperty() Method
- JavaScript Object defineProperties() Method
- JavaScript Object entries() Method
- JavaScript Object freeze() Method
- Javascript Object getOwnPropertyDescriptor() Method
- JavaScript WeakSet
- JavaScript Array sort() Method
- JavaScript Array splice() Method
- Javascript Object getOwnPropertyDescriptors() Method
- JavaScript WeakMap
- JavaScript Interview Questions (2021)
- Javascript Object getOwnPropertyNames() Method
- JavaScript Benchmark: performance.now
- Javascript Object getOwnPropertySymbols() Method
- JavaScript handler
- JavaScript Reflect
- javascript regexp
- Javascript Object getPrototypeOf() Method
- JavaScript Array concat() Method
- Javascript Object is() Method
- JavaScript Array every() Method
- Javascript Object preventExtensions() Method
- JavaScript Array fill() Method
- Javascript Object seal() Method
- Javascript Object setPrototypeOf() Method
- Javascript Object values() Method
- JavaScript Reflect apply() Method
- JavaScript Reflect construct() Method
- JavaScript Reflect defineProperty() Method
- JavaScript Reflect deleteProperty() Method
- JavaScript Reflect get() Method
- JavaScript Reflect getOwnPropertyDescriptor() Method
- JavaScript Array filter() Method
- JavaScript Reflect getPrototypeOf() Method
- JavaScript Array find() Method
- JavaScript Reflect has() Method
- JavaScript Array findIndex() Method
- JavaScript Reflect isExtensible() Method
- JavaScript Array forEach() Method
- JavaScript Date setUTCMinutes() Method
- JavaScript Reflect ownKeys() Method
- JavaScript Array includes() Method
- JavaScript Reflect preventExtensions() Method
- JavaScript indexOf and lastIndexOf
- JavaScript Array indexOf() Method
- JavaScript Reflect set() Method
- JavaScript Array join() Method
- JavaScript Reflect setPrototypeOf() Method
- JavaScript Array lastIndexOf() Method
- JavaScript Symbol for() Method
- JavaScript charAt: Get Char From String
- JavaScript Set add() Method
- JavaScript Set clear() Method
- JavaScript String indexOf() Method
- JavaScript Set delete() Method
- JavaScript Set entries() Method
- JavaScript Initialize Array
- JavaScript Set forEach() Method
- JavaScript Set has() Method
- JavaScript Set values() Method
- JavaScript String charAt() Method
- JavaScript String charCodeAt() Method
- JavaScript Array map() Method
- JavaScript String concat() Method
- JavaScript Array pop() Method
- JavaScript String toLowerCase() Method
- JavaScript Array push() Method
- JavaScript String toLocaleLowerCase() Method
- JavaScript Array reverse() Method
- JavaScript String toUpperCase() Method
- JavaScript Array shift() Method
- JavaScript String toLocaleUpperCase() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray fill() Method
- JavaScript Array slice() Method
- JavaScript String toString() Method
- JavaScript Array unshift() Method
- JavaScript String valueOf() Method
- JavaScript Function apply() Method
- JavaScript Symbol keyFor() Method
- JavaScript Symbol toString() Method
- JavaScript string
- JavaScript Date
- JavaScript math
- JavaScript Symbol hasInstance Property
- JavaScript String substring() Method
- JavaScript String slice() Method
- JavaScript Symbol isConcatSpreadable Property
- JavaScript Equals: 2, 3 Equals Signs
- JavaScript Symbol match Property
- JavaScript Symbol prototype Property
- JavaScript encodeURI Examples
- JavaScript Symbol replace Property
- JavaScript Symbol search Property
- JavaScript Symbol toStringTag Property
- JavaScript handler defineProperty() Method
- JavaScript handler ownKeys() Method
- JavaScript handler preventExtensions() Method
- JavaScript Function bind() Method
- JavaScript Symbol unscopables Property
- JavaScript TypedArray copyWithin() Method
- JavaScript Function call() Method
- JavaScript Symbol split Property
- JavaScript Function toString() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray entries() Method
- JavaScript Date getDate() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray every() Method
- JavaScript arguments (Function)
- JavaScript Date setUTCSeconds() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray filter() Method
- JavaScript Date getFullYear() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray find() Method
- JavaScript handler set() Method
- JavaScript Date getHours() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray findIndex() Method
- JavaScript Date getMilliSeconds() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray forEach() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray includes() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray indexOf() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray join() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray reduce() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray keys() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray lastIndexOf() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray map() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray reduceRight() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray reverse() Method
- JavaScript Date getMinutes() Method
- Not Found: javascript-date-setfullyears-method
- JavaScript Date setHours() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray set() Method
- JavaScript Date getMonth() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray slice() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray sort() Method
- JavaScript Date getSeconds() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray some() Method
- JavaScript Date getUTCDate() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray subarray() Method
- JavaScript parseInt Examples
- JavaScript Date getUTCDay() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray values() Method
- JavaScript Date getUTCHours() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray toLocaleString() Method
- JavaScript Date getUTCMinutes() Method
- JavaScript TypedArray toString() Method
- JavaScript Date getUTCMonth() Method
- JavaScript WeakMap delete() Method
- JavaScript WeakMap get() Method
- JavaScript WeakMap has() Method
- JavaScript WeakMap set() Method
- JavaScript WeakSet add() Method
- JavaScript Array Examples
- JavaScript WeakSet delete() Method
- JavaScript WeakSet has() Method
- JavaScript Array copyWithin() Method
- JavaScript Date setUTCDate() Method
- JavaScript Substring Examples
- JavaScript switch Statement
- JavaScript Date getUTCSeconds() Method
- Not Found: javascript-date-setdate-method
- Not Found: javascript-date-setday-method
- JavaScript Date setMilliseconds() Method
- JavaScript Date setMinutes() Method
- JavaScript Date setSeconds() Method
- JavaScript Date setUTCMonth() Method
- JavaScript Date toDateString() Method
- JavaScript Date toISOString() Method
- JavaScript Date toJSON() Method
- JavaScript Date toString() Method
- JavaScript Date toTimeString() Method
- JavaScript Date toUTCString() Method
- JavaScript Date valueOf() Method
- JavaScript handler apply() Method
- JavaScript String
- JavaScript handler construct() Method
- JavaScript handler deleteProperty() Method
- JavaScript handler get() Method
- JavaScript handler getOwnPropertyDescriptor() Method
- JavaScript Date getDay() Method
- Learn JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript toLowerCase Examples
- JavaScript Int32Array Examples
- JavaScript JSON.parse Examples
- JavaScript Multiple Return Values
- JavaScript Symbol
- JavaScript Keywords
- JavaScript replace Examples
- JavaScript handler getPrototypeOf() Method
- JavaScript handler has() Method
- JavaScript String substr() Method
- JavaScript variable
- JavaScript Objects
- JavaScript array
- JavaScript handler isExtensible() Method
- JavaScript handler setPrototypeOf() Method
- JavaScript JSON parse() Method
- Not Found: javascript-date-setutcmilliseconds-method
- JavaScript JSON stringify() Method
- JavaScript Map clear() Method
- JavaScript Map delete() Method
- JavaScript JSON
- JavaScript String search() Method
- JavaScript String match() Method
- JavaScript Map entries() Method
- JavaScript Map forEach() Method
- JavaScript Map get() Method
- Not Found: javascript-date-setutcday-method
- JavaScript Date setUTCHours() Method
- JavaScript Map has() Method
- JavaScript Map keys() Method
- JavaScript Map set() Method
- JavaScript Map values() Method
- JavaScript Math abs() Method
- JavaScript Math acos() Method
- JavaScript Map
- JavaScript Math asin() Method
- JavaScript typeof String, Number
- JavaScript Math atan() Method
- JavaScript Math cbrt() Method
- JavaScript for Loop Examples
- JavaScript Math ceil() Method
- JavaScript Math cos() Method
- JavaScript Math cosh() Method
- JavaScript Math exp() Method
- JavaScript Example
- JavaScript comment
- JavaScript global variable
- JavaScript data types
- JavaScript operators
- JavaScript if else
- JavaScript switch
- JavaScript Loops
- JavaScript function
- JavaScript Length Examples
- JavaScript Math floor() Method
- JavaScript Math hypot() Method
- JavaScript Sort String Arrays
- JavaScript Math log() Method
- JavaScript Linked List Example
- JavaScript Math max() Method
- JavaScript split Examples
- JavaScript Math min() Method
- JavaScript function Lookup Table
- JavaScript Math pow() Method
- JavaScript Math random() Method


